VACUUM INSULATED TUBING
VACUUM INSULATED TUBING
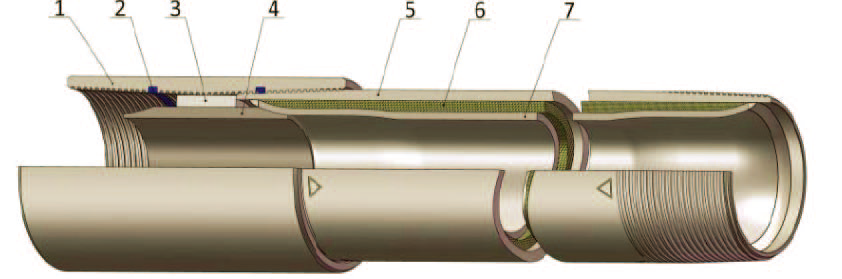
1. Coupling 2. Optional Seal ring 3. Insulation sleeve 4. Insert
5. Outer tube 6. Insulating material 7. Inner tube
VIT technology has now moved to enhance the steam injection process in SAGD type oil wells as well as in reducing wax buildup in producing wells. .
In SAGD application, VIT allows for delivered steam to the injection point at a higher temperature resulting in a more cost effective operation.
For the prevention of Paraffin or wax buildup which occurs when the producing fluid falls below the cloud point, VIT maintains the fluid temperature and reduces the occurrence of paraffin buildup thus reduction costly well shut down and production loss.
Gas absorbing materials are packed inside the annulus to clean up harmful gas and maintain good insulating property in service.

During assembly, a vacuum port is drilled into the outer tube, and both tubes are blasted to remove scale. The inner tube is then wrapped with foil and hydrogen-scavenging ©"getter" is
installed. Next, centralizers are mounted on the inner tube, which is subsequently run into the outer tube and fillet-welded in place. A vacuum pump is then attached to a port in the outer tube, and the entire assembly is run into a convection oven and heated.
The heat activates the getter, which vaporizes any contaminants in the annular space. The annulus is then voided by the vacuum pump. Upon completion of this stage, the vacuum pump is removed, the port is plugged and welded, and the thermal efficiency of the assembly is measured to verify that the desired thermal properties were achieved. The completed assembly is threaded (with premium threads, if desired) and shipped to its destination.
|
OD |
ID |
Connection |
Coupling OD |
Insulating Grade * |
Pipe Grade |
|
177.8 |
139.7 |
API or Semi Premium |
194.5 |
B, C |
J, N, L, P |
|
139.7 |
88.9 |
API or Semi Premium |
153.7 |
D, E |
J, N, L, P |
|
139.7 |
101.6 |
API or Semi Premium |
153.7 |
D, E |
J, N, L, P |
|
127 |
76 |
API or Semi Premium |
141.3 |
C, D, E |
J, N, L, P |
|
114.3 |
62 |
API or Semi Premium |
127 |
C, D, E |
J, N, L, P |
|
114.3 |
76 |
API or Semi Premium |
127 |
C, D, E |
J, N, L, P |
|
88.9 |
40.9 |
API or Semi Premium |
108 |
B, C, D, E |
J, N, L, P |
|
INSULATING |
B |
C |
D |
E |
|
k-factor |
0.06>λ≥0.04 |
0.04>λ≥0.02 |
0.02>λ≥0.006 |
0.006>λ≥0.002 |
